Health and Beauty
For most cases, treatment for Arthritis depends on the diagnosis. Generally, the desired outcomes are to relieve joint pains, preserve joint function and prevent deformities. Surgery may be necessary. Medication will depend on the underlying condition.
1. Pain relief. Analgesics (painkillers) are commonly used in the relief of joint pains. They can be simple analgesics or drugs termed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs are effective but have the common side effect of gastric irritation. The elderly are especially at risk of bleeding in the stomach or intestine.
*Adequate rest and weight reduction, especially in the case of osteoarthritis, can also help to relieve pain. Heat therapy relieves many patients suffering acute or chronic pain.
2. Preserving joint function and preventing deformities. Early proper treatment of specific conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can prevent deterioration and permanent joint damage leading to deformities. See a specialist early for treatment. Physiotherapeutic exercises, including hydrotherapy, are useful in treating acute pain and maintaining joint function.
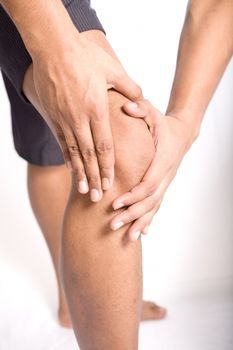
3. Surgical intervention. At times, joint deformities occur causing chronic persistent pain. They can also severely affect mobility, thus resulting in a poor quality of life. Joint replacement surgery may have to be performed on individuals affected.
4. Diet. Dietary restriction generally does not play a significant role in alleviating joint pains except for gouty arthritis. Gouty arthritis patients need a low-purine diet. Otherwise, arthritis patients should have a balanced diet. There are also some Natural Joint Pain Relief options available for patients who prefer natural treatments.
Beauty Health Care
Can I apply Chinese ointment for arthritis ?
Topical applications such as Chinese ointment are useful as an adjunct to the main treatment. They act by producing a counter-irritation, namely converting a pain to a warm feeling which is more bearable. Their usefulness derives from the potential benefit of helping to reduce the dosage of analgesic needed to treat joint pains, hence lowering the risk of side effects. However, they should not and cannot replace the main treatment, unless the condition is very mild. Note that all topical applications, including Chinese ointments, can cause allergic reactions in the skin if the individual is allergic to the contents of the ointment. Ointments should not and cannot replace the main treatment, unless the condition is very mild.
What about acupuncture? Is it effective for arthritis?
The Chinese have used acupuncture in the treatment of various conditions, including rheumatism, for thousands of years. Hence it is a “tested” treatment. However, its use in the treatment of arthritis, especially the severe forms, is usually as an adjunct to the main treatment, to help control pain.
The effectiveness of acupuncture also depends on several factors, including the experience of the acupuncturist, the cause of the joint pains and the severity of the condition. Severe chronic pain requiring surgical intervention usually does not respond well to acupuncture treatment alone. It is therefore prudent to discuss with the attending doctor how acupuncture may play a part in the overall treatment. Beware also any acupuncturist who claims acupuncture to be a panacea for all pains. It is prudent to discuss with the attending doctor how acupuncture may play a part in the overall treatment of arthritis.